Pillars/Thematic Areas
The structure of the DPG encompasses five thematic domains, each organized under specific sectoral activities. Each domain consists of clusters that function within that specific sector. Currently, the DPG structure includes (at this point 17) Joint Working Groups. These JWGs collaborate to formulate and oversee sector investment plans and funding strategies. In their respective sectors, the JWGs play a key role in coordination.
In Ethiopia, the government, and Development Partners (DPs) have established a robust dialogue architecture to address aid cooperation challenges and achieve common development goals. Sector Working Groups (SWGs) are one of the important parts of this structure. As part of the dialogue structure, 17 JWGs have been established. Working Groups on Urban Development, on Innovation, ICT and Digital Economy is expected to be set up soon) under the 5 thematic areas/pillars. Governance and the Conflict & Development Cooperation working groups are technical working groups.
The JWGs are Joint Working Groups – are spaces that allow technical dialogue between government and development partners on strategic sectoral issues. They are normally chaired by a high-level representative of the lone ministry in charge of the specific sector, and cochaired by one or two representatives of DPG agencies supporting that sector. The JWGs are expected to agree on sectoral priorities – in line with the National Development Plan -, coordinate joint action in support to those priorities, develop and monitor sector investment programs, identify development and investment gaps for the sector and mobilize resources and propose investments to close those gaps. In addition, to the extent possible, and depending on the nature of the sector, they are expected to promote collaboration of humanitarian, development and peacebuilding actors and to address root causes of humanitarian need. The JWGs aim to improve coordination, alignment, and accountability in the delivery of development assistance.
The JWGs are responsible for planning and monitoring investments across different sectors. They work diligently to ensure that these investments are in line with the goals and objectives outlined in the TYDP. This alignment is crucial for ensuring the effective and efficient use of resources.
In addition to planning and monitoring investments, the JWGs are also tasked with reporting their progress and results in a regular and transparent manner. This reporting process is an integral part of ensuring accountability and tracking the progress of development initiatives.
The JWGs are not static entities. They are dynamic and adaptable, capable of incorporating additional stakeholders based on the specific needs of the sector. This flexibility allows the JWGs to respond effectively to changing circumstances and challenges.
One of the innovative approaches that the JWGs are exploring is the use of public-private partnerships to finance their activities. This approach leverages the resources and expertise of the private sector, potentially leading to more sustainable and effective development initiatives.
To guide their work, the JWGs have standard terms of reference, work plans, and results frameworks. These tools provide a clear roadmap for the JWGs, outlining their responsibilities and expectations.
The JWGs meet at least four times a year to discuss their progress and plan their future activities. They also communicate their work through various channels, ensuring that all stakeholders are kept informed of their activities and progress.
The JWGs play a crucial role in driving development cooperation in Ethiopia. They work to align efforts with the TYDP, monitor and plan investments, report on their progress, and explore innovative financing methods. Through their work, the JWGs contribute to the effective and efficient use of resources, ultimately driving Ethiopia’s development forward.
Development Partner Group - Structure
The structure of the DPG encompasses five thematic domains, each organized under specific sectoral activities. Each domain consists of working groups that function within that specific pillar. Currently, the DPG structure includes (at this point 17) Joint Working Groups (JWGs).
These JWGs are expected to collaborate to formulate and oversee sector investment plans and funding strategies. They work to align efforts with the Ten Year Development Plan (TYDP), monitor and plan investments, report on their progress, and explore innovative financing methods.
Through their work, the JWGs contribute to the effective and efficient use of resources, ultimately driving Ethiopia’s development forward. The 5 pillars are aligned with the TYDP. The working groups provide technical support for the realization of the national development plan.
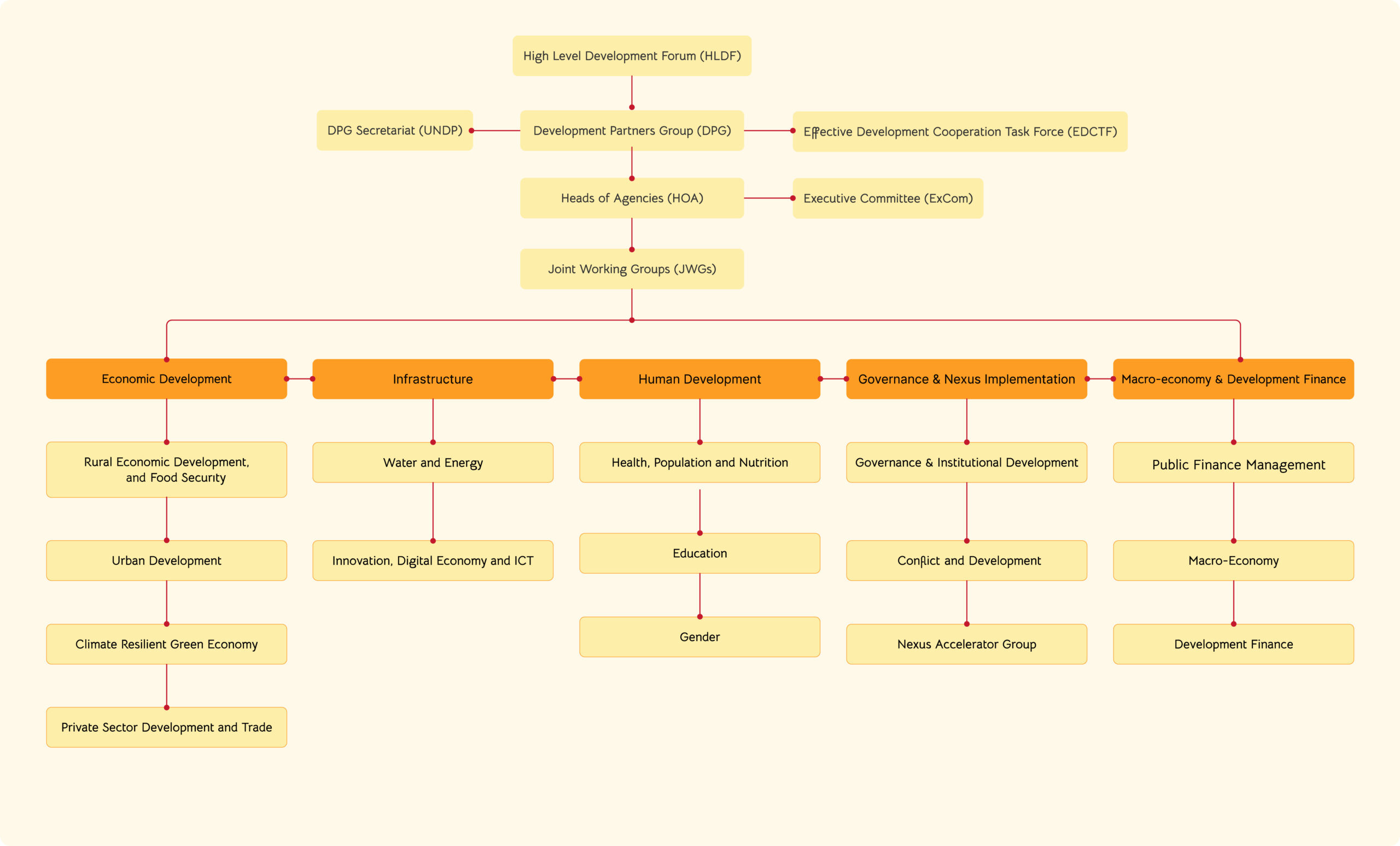
Economic Development Pillar
This pillar consists of four Joint Working Groups (JWGs) which are Rural Economic Development and Food Security (REDFS), Urban Development, Private Sector Development and Trade, and Climate Resilient Green Economy Forum.
Infrastructure Pillar
This pillar is composed of three JWGs, namely Transport, Water & Energy, and Innovation, Digital Economy & ICT.
Human Development Pillar
This pillar includes four JWGs, which are Health, Population and Nutrition, Education, Gender, and Basic Service Delivery.
Governance and Nexus Implementation Pillar
This pillar is made up of three JWGs, namely Governance & Institutional Development, Conflict, Development and Triple Nexus, and Nexus Accelerator Group.
Macro Economy and Development Finance Pillar
This pillar consists of three JWGs, which are Public Finance Management (PFM), Macro Economy, and Development Finance.